DASH Diet | What You Need to Know
How & Why the DASH Diet Works from the Researchers Who Designed It
Including recipes, resources and meal plans
 1. What is the DASH Diet? Why isn’t it better known as a weight loss diet?
1. What is the DASH Diet? Why isn’t it better known as a weight loss diet?
The original DASH Diet design wasn’t focused on weight loss, although the diet does help with weight loss. In fact, the DASH Diet was developed by a team of more than 160 health care professionals and researchers who aimed to discover a dietary “pattern” that lowered blood pressure and still tasted good. They found that a dietary solution to high blood pressure was not only possible, it was very successful.
The "DASH" Diet stands for “Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension,” which is why some call it a high blood pressure diet.
Pro Tip: For those interested primarily in weight loss, our weight loss calculator is available here.
2. Who developed the DASH Diet?
The DASH Diet Collaborative Group members include a world-class group of doctors, registered dietitians and PhD nutrition researchers.
Pennington Biomedical’s Dr. George Bray, Dr. Donna Ryan and Dr. Catherine Champagne, RD, LD, were among the lead developers and researchers of the diet. The successful study results were published in this 1997New England Journal of Medicine publication, which has been cited by other researchers almost 6,000 times since original publication.
Dr. John Kirwan, Executive Director of Pennington Biomedical: “The DASH Diet was developed by some of our Pennington Biomedical pioneers, with Dr. George Bray, Dr. Donna Ryan and Dr. Catherine Champagne among the lead developers in the DASH Diet Collaborative Research Group. Thirty years after its development, the DASH Diet has stood the test of time and is a proven eating plan with numerous health benefits. Pennington Biomedical is proud of our history and role in the DASH Diet.”
3. Does the DASH Diet really work?
Yes! The U.S. News & World Report team of science and nutrition experts has listed the DASH Diet among its top diets for many years and it has consistently ranked as the top heart-healthy eating plan. They recognize its long-term success in reducing high blood pressure, improving the health of those with diabetes and as a weight loss diet that also improves health.
In adition, the American Heart Association assessed and scored the heart healthiness of popular dietary patterns, and the DASH Diet – developed in part at Pennington Biomedical Research Center – received a perfect score as the top heart-healthy eating plan.
- The blood pressure reduction in original DASH Diet study participants was linked to a 27% less stroke rate and a 15% less heart disease rate.
- Study participants on the DASH Diet also saw their total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol numbers lower than those on a regular diet.
- The DASH Diet is not considered a low-carb diet. Even so, participants on the eating plan who were fed more carbohydrates than the regular comparison diet did not see an increase in triglycerides.
Dr. Catherine Champagne: "“The DASH Diet is a healthy eating pattern that is easy to stick with, and it works for the whole family. For the past 15 years, DASH has been ranked at or near the top of the U.S. News & World Report rankings because it is scientifically proven to lower blood pressure, lower the risk of stroke, lowers the risk of cardiovascular events, and works to improve metabolism regardless of your size.”
4. Are there any certain foods the DASH Diet recommends you avoid?
Besides reducing sugar sweetened beverages and sodium, the DASH Diet is instead focused on increasing fruits, vegetables, whole grains and dietary fiber.
The food plan in the DASH Diet includes:
- Lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein and low-fat dairy
- Foods high in potassium – fruits, vegetables and potatoes
- Foods high in magnesium – nuts, leafy green vegetables
- Salt or sodium targets between 1500 – 2300 mg/day maximum (and the lower in sodium, the better!)
- No sugar sweetened beverages and very little additional "sweets" or desserts
- No supplements were used
5. How much does the DASH Diet cost to follow?
The diet is absolutely free of charge. These resources are available to anyone. In fact, it’s ranked by US News & World Report as an easy diet to follow in part because the foods are easily accessible in most grocery stores or farmer’s markets.
US NEWS & WORLD REPORT BEST DIET RANKINGS
Beginning in 2011, the DASH Diet was ranked the #1 diet overall for eight years in a row. As of 2025, the DASH Diet was ranked in serval categories by U.S. News & World Report:
- Best Diets Overall (No. 2)
- Best Heart-Healthy Diets (No. 1)
- Best Diets for High Blood Pressure (No. 1)
- Best Diets for High Cholesterol (No. 2)
- Best Diabetes Diets (No. 3)
- Best Diets for Prediabetes (No. 2)
- Best Diets for Healthy Eating (No. 2)
- Best Diets for Gut Health (No. 2)
- Easiest Diets to Follow (No. 3)
- Best Diets for Mental Health (No. 4)
- Best Diets for Menopause (No. 4)
- Best Diets for Arthritis (No. 4)
- Best Diets for Brain Health (No. 4)
Nationally recognized expert panelists scored 38 diets in 21 categories. Read more about the DASH Diet 2024 U.S. News & World Report rankings.
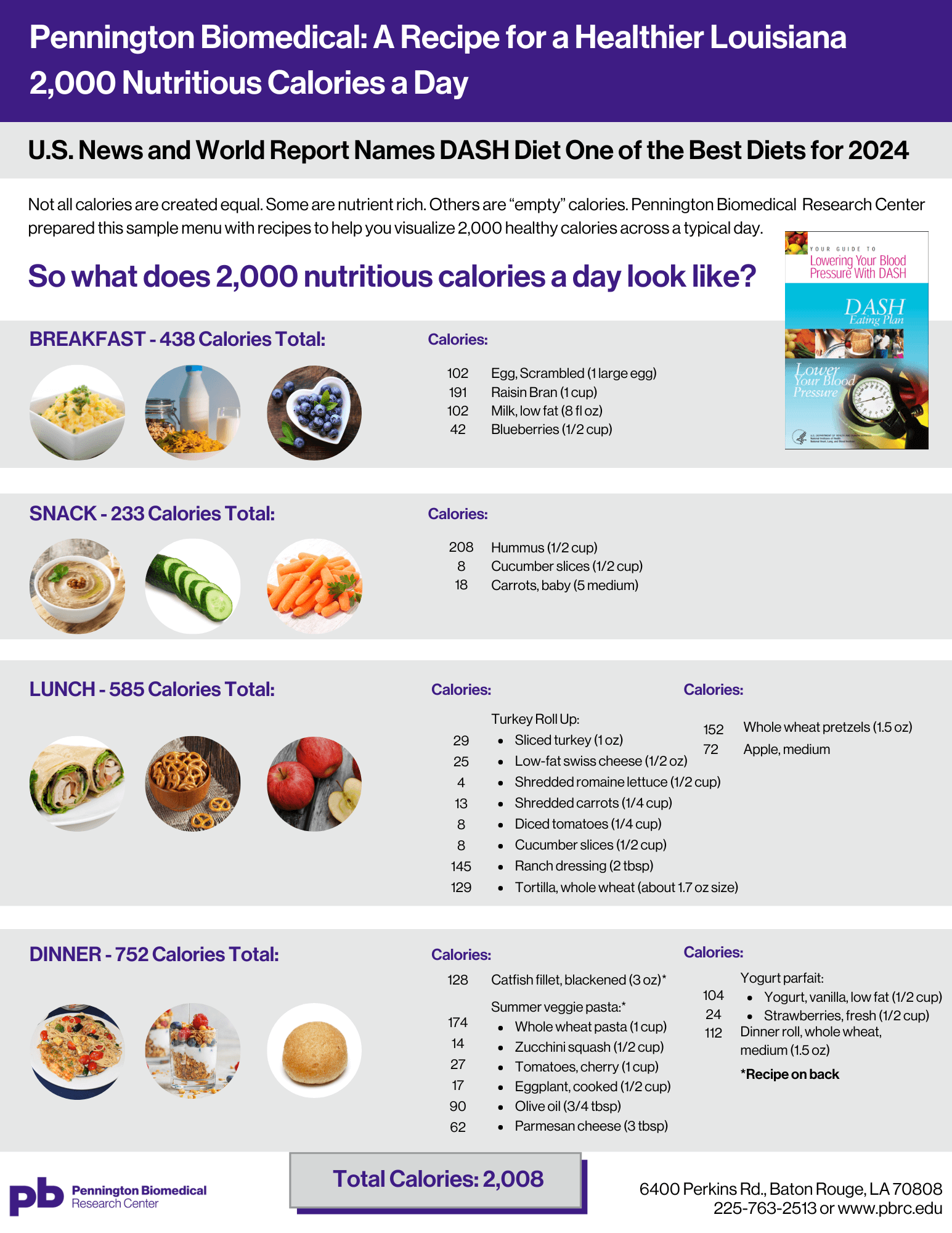
Bonus: DASH Diet Menus and Eating Plans
- A 20 page DASH Diet pdf booklet including DASH menus and recipes is available for download free of charge.
- A 2,000 Calorie Day Menu with DASH Diet recipes can be found on our blog site.
- The Dash Diet Eating Plan: A four-page quick-glance pdf of DASH Diet foods developed by Pennington Biomedical registered dietitians and our partners from the LSU Ag Center.
- Dr. Catherine Champagne reviews the benefits of the DASH diet in this short video.
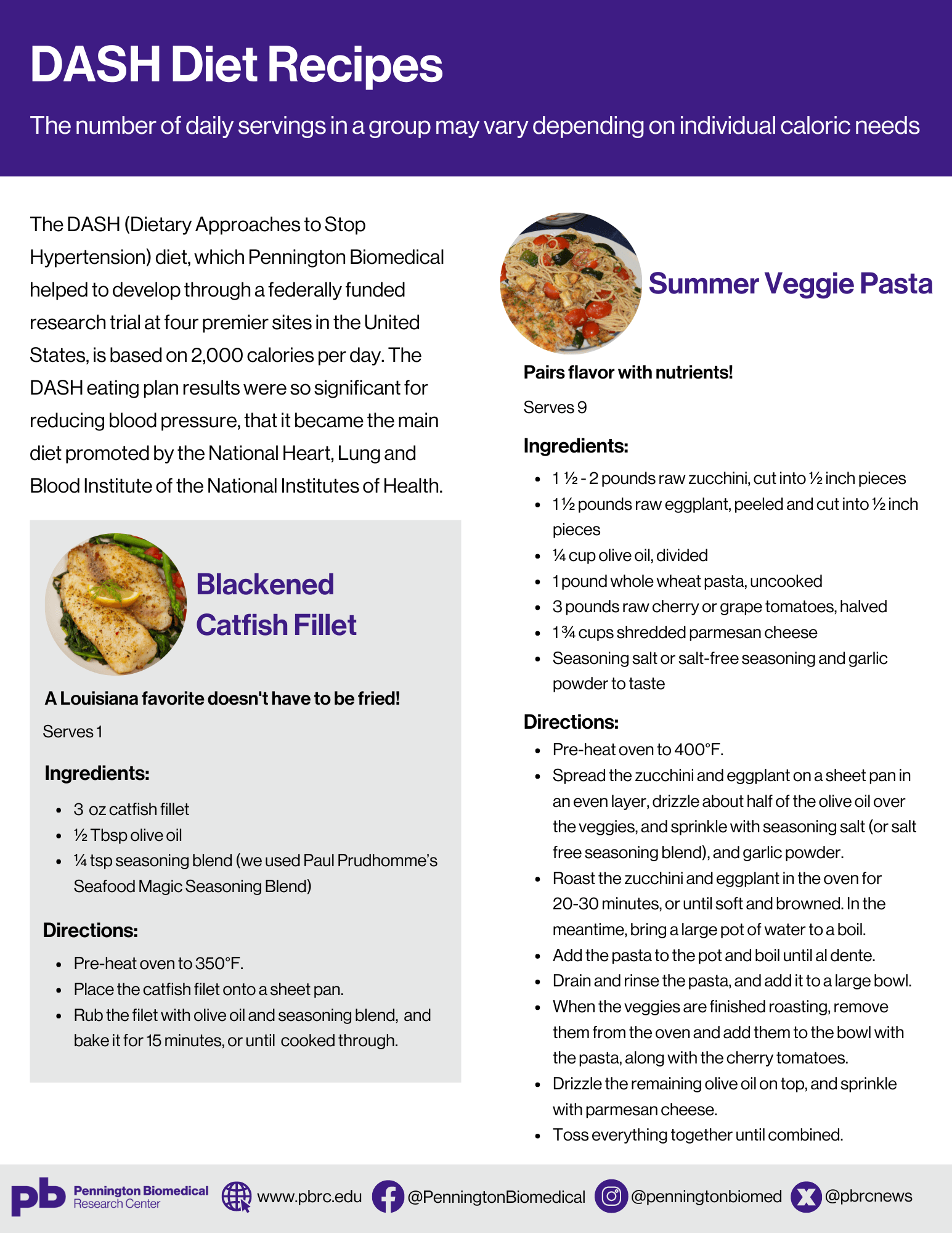
- Here are two sample DASH Diet recipes developed by the Pennington Biomedical Metabolic Kitchen: Renee Puyau, Director; and Catherine Champagne, RD, LD, PhD. Dr. Champagne served on the original DASH Diet Collaborative Group.
Acknowledgments:
The DASH Diet study was funded by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute.
The DASH Diet Collaborative Group is composed of scientists, registered dieticians
and physicians from these institutions:
Boston University School of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical
School, Duke University Medical Center, Johns Hopkins University, Kaiser Permanente
Center for Health Research, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, Pennington Biomedical
Research Center, Louisiana State University, Virginia Polytechnic Institute.





